
When, how and why to wash roots
In the world of self-cultivation, there seems to be a debate on cannabis root washing. Opponents believe that doing so before harvest will deprive roots of vital nutrients. On the other side of the divide,…
Iberian Peninsula express shipping
0€ Orders over 60€
*6€ orders under 59€
East, West, South Europe express shipping
0€ Orders over 150€
*18€ orders under 149€
North Europe express shipping
0€ Orders over 160€
*20€ orders under 159€
Ireland, Norway, UK normal shipping
0€ Orders over 60€
*6€ orders under 59€
Rest of the world normal shipping
0€ Orders over 180€
*25€ orders under 179€
Shipping costs can be confirmed in your shopping cart.
For additional shipping methods, please reach out through info@kannabia.com.


*Website protected by SSL.
**Not available in all regions.
*Your coupon will be sent via email.
*Should you have any question, comment or feedback, please do not hesitate to contact us.
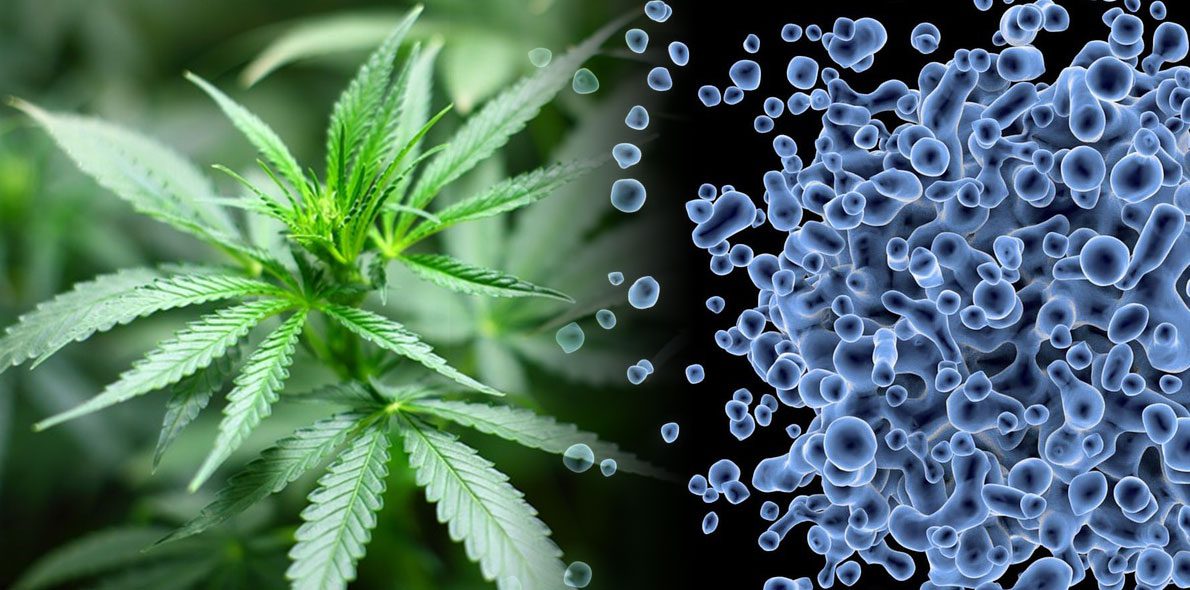

We are going to cover types of fungi that can appear in our cannabis culture, what the conditions for them to appear are, and how we can prevent them.
Fungi are the disease most feared by growers, because they can irreversibly damage all production, having to literally throw away so many months of work. We must not only deal with the nutrition of plants, but we must also take into account factors such as temperature, humidity and ventilation of the place of cultivation. The fungi are inactive in the form of spores waiting for that perfect environment to develop and make all plants sick.
There are many species of mushrooms, but these varieties are the ones that most affect the cultivation of cannabis.
It is the most common fungus, also called white mold, which usually appears in spaces that exceed 60% humidity and temperatures that exceed 25 degrees. The drastic changes in atmospheric conditions will make the spores proliferate and are very difficult to eradicate later, therefore, always try to prevent.

This fungus begins to develop on the leaves of plants in the form of white powder, and begins to expand rapidly in stems and flowers.
Oidium generates roots that absorb nutrients from the plant to survive, once the flowers are affected by fungi are no longer suitable for consumption, since we run the risk of catching the fungus. While powdery mildew expands more slowly than other types of mushrooms, the consequences are terrible! Once it is installed it is very difficult to attack it with organic products. Personally, what helped me was a systemic fungicide with a sulphur base and a total and complete disinfection of the place of cultivation. In addition to cutting all my plants, the powdery mildew spore can remain alive stuck on a wall for 2 years, so be aware of all forms of prevention! Sulphur-based remedies cannot be placed under the sun and at temperatures above 27º Celsius.
Another fungus most feared by all. This fungal pathogen and endoparasite, enters through openings or wounds in the same plant. The spore germinates within the tissue and may even be inactive until the conditions are right for the beginning of its expansion. Its detection is easy since hairy and grey areas start to be visible. Its development is very fast and, if not detected in time, can cause in a few days the total loss of flowers.

Once it is installed, I recommend removing the affected parts with the maximum of care so that the spore does not fly while you are cleaning and that it does not contaminate other flowers. It is recommended to maintain humidity below 57% and temperatures below approximately 27ºC.
This fungus appears in spring and also in autumn with abundant humidity and rains. It can be seen in plants that are about to start the flowering cycle. The rust reproduces and expands rapidly in leaves. The colour may vary from orange, to red or yellow. Once it is installed, we have to remove all the affected parts and cut the cycle to prevent its reproduction. We can attack with remedies based on cupric sulphate andhydrated lime, copper sulphate and lime.

As an endoparasite such as the fungus botrytis, mildew also achieves its development in the inner part of the plants. The resistance of this fungus is superior since it can live up to 2 years regardless of the conditions. Therefore, be ALWAYS very careful with the hygiene of the cultivation area, cleanliness is essential to avoid this kind of diseases to attack our plants. We can easily detect it as it begins to attack the leaves and we start to visualise brown and translucent spots. If we allow it to advance it could end up killing the plant. To eradicate it, they must be used with powerful fungicidal chemicals that are injected into the flow of plant sap. This can clearly affect the final production due to the metabolic changes that the plants undergo when treated. The ventilation and the cleanliness of the plant, as we said, is a fundamental part to avoid headaches.

This type of fungus inhabits the soil, affects the stem, the root and also produces vascular wilt. It lives on decomposing organic matter. Fusarium oxysporum affects the stem, being able to detect it by the brown spot it causes. The fusarium solani produces the rot of root. We can detect it since the branches begin to dry and to become brown. It can kill the plant in a matter of days.
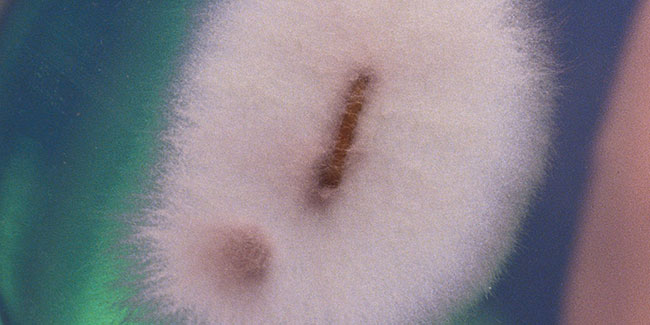
We have to water it with water that has not been stagnant, or several days at rest. In no more than 24 hours we will have eliminated the chlorine from the water and we will avoid this type of problem in our crop.
The maximum and minimum temperatures for it to develop are between 10ºC and 30ºC approximately and the optimum reproduction is at 20 / 25ºC. To prevent this, the issue of hygiene is also crucial, as in the previous cases. We must try to remove rotten leaves from the ground and keep the plants with a correct hygiene and optimal ventilation.
The best preventive is the application of trichoderma from the seedling and in each transplant.
The use of propolis for agricultural use will help keep these fungi away and raise the immunity of the plant, making it much more resistant to this type of pathogen.
Natural enemies against fusarium are: seed extract of Citrus paradisi, streptomyces griseoviridi and bacillus subtilis.
Although each person has her/his specific methods or similar to mine, we can say as useful preventive measures for all cases, that it is essential to carry out a complete hygiene between harvests; disinfecting the pots, gardening tools and remove, in addition, any plant remains such as dead leaves, branches or even dead insects in the substrate. You can also use organic preventive or chemical based fungicides in some cases. Do not forget to take care of ventilation, humidity and temperature (around 25 degrees and 50% humidity) of the growing environment.
I hope this post helps you in the prevention of these unwanted fungi and that your crops are always prosperous and of high quality!